You can learn through various methods such as reading, memorizing, using flashcards, and more. However, one of the best ways to learn is by practicing and taking tests! So, let’s practice.
Here are some high-quality, up-to-date questions for the CFA Level 3 exam on yield curve movements.
Enjoy!

In mid-2024, the global economy faces mixed signals. Even though inflation in England reached the target in May 2024 for the first time, the Bank of England (BoE) has kept its Bank Rate steady at 5.25%, amid persistent but slowly decreasing inflation. Moreover, the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) a few months ago decided to increase its rates once more to combat a sudden rise in inflation, setting the cash rate at 4.35%. Meanwhile, the Federal Reserve in the U.S. is closely monitoring economic indicators, signaling potential rate cuts if the economy slows further.
- Bank of England (BoE) Bank Rate – 5.25%
- England inflation (May 2024) – 2%
- Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) – 4.35%
Alice anticipates that the Fed will cut rates by 0.5% over the next 9 months. She expects short-term rates to decrease significantly and long-term rates to fall modestly. Also, she notices that the market expects 1 rate cut in the next 9 months.
Bob believes that the BoE’s decision to maintain high rates will attract international investors seeking higher yields, leading to an brisk increase in demand for long-term bonds. Also, he expects that 1-year yields will slowly and slightly reflect future rate cuts. Mid-term rates will follow proportionally.
Carla predicts that the RBA’s recent rate hike will lead to a stronger Australian dollar, prompting international capital flows into Australia. She expects that this effect will be most influential on Australian mid-term rates.
Daniel is concerned about potential stagflation in the U.S., where inflation remains high but economic growth stagnates. He expects severe stagflation that heavily undermines future growth expectations and forces the Fed to further increase its rate by 1%. In his opinion, this will cause an even deeper yield curve inversion than it is now.
What strategy is most likely the best for Alice to implement based on her expectations?
- Increase duration of the portfolio.
- Position for a positive butterfly twist.
- Short Fed Fund futures.
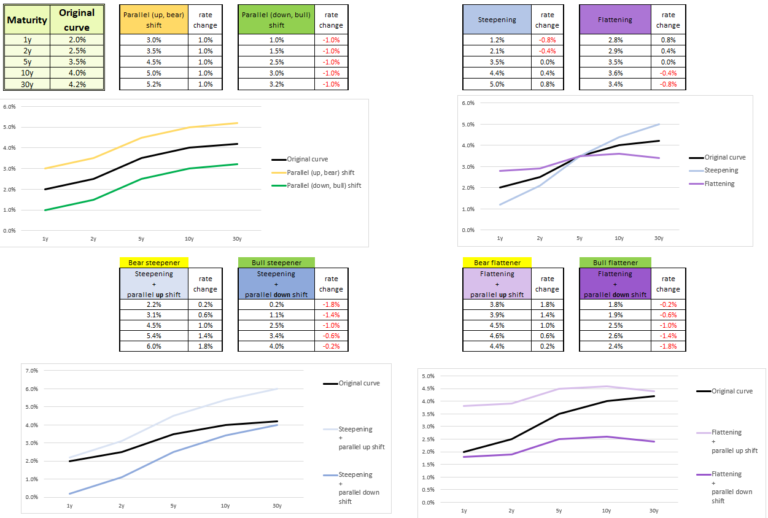
What yield curve movement does Bob expect due to the BoE’s high rates?
- Bull flattening
- Bear steepening
- Bull steepening
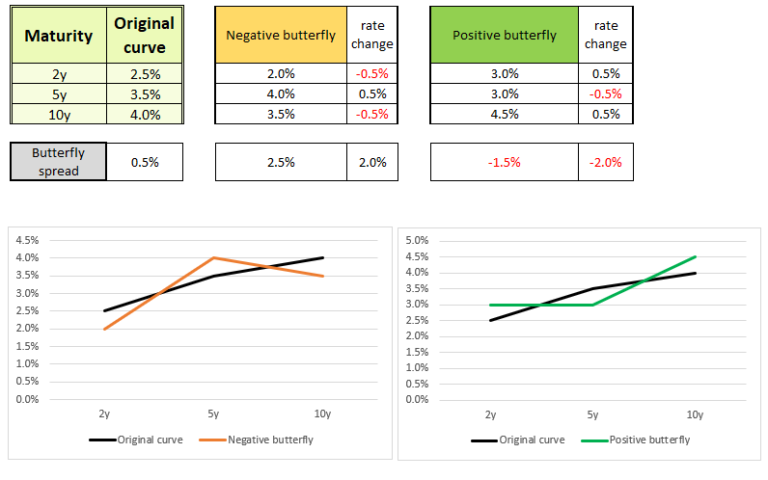
According to Carla’s expectations, what will be the effect on the butterfly spread on the RBA’s yield curve?
- Increase
- Decrease
- No change
What’s the name of the move on the yield curve that Daniel expects?
- Bull steepening
- Bear flattening
- Bear steepening
Answers and explanation
What strategy is most likely the best for Alice to implement based on her expectations?
- Increase duration of the portfolio
- Position for a positive butterfly twist
- Short Fed Fund futures
Explanation:
- Duration:
- Rates Falling: When interest rates are expected to fall, bond prices typically rise, and bonds with longer durations (longer maturities) benefit more from this price increase.
- Increasing Duration: By increasing the duration of her portfolio, Alice is positioning her investments to gain more from the expected decline in interest rates.
- Positive butterfly twist: This yield curve move means short-term and long-term rates go up, (while intermediate-term rates go down,) which isn’t the case here. Positive butterfly twist is typically described as the yield curve becoming more “humped” in the middle or “bowing” outward.
- Short Fed Fund futures: Alice expects 2 rate cuts, while the market is expecting fewer—just one rate cut. Fed Fund futures are quoted as 100 minus the expected federal funds rate. For example, if the market expects the federal funds rate to be 5% (implied rate), the futures contract would be quoted at 95.00 (100 – 5.00 = 95.00). If Alice’s expectation of rate cuts materializes, the implied interest rate will be lower. Consequently, the futures price will increase because the futures price = 100 – implied rate. She might consider going long Fed Fund futures.
What yield curve movement does Bob expect due to the BoE’s high rates?
- Bull flattening
- Bear steepening
- Bull steepening
Explanation:
- High Rates Attracting Investors: Bob believes that the high rates will attract international investors to long-term bonds, increasing their demand and hence driving their yields down.
- 1-Year Yields Reflecting Future Rate Cuts: Bob expects short-term yields (1-year yields) to slowly and slightly reflect the anticipated future rate cuts, meaning short-term rates may decrease slightly.
- Correct answer – Bull flattening: Rates are falling, which is bull movement. Long end of the yield curve is falling more rapidly then short term, which means difference between changes in long-term and short-term rates is negative. Don’t let the chart fool you (graphically it looks like steepening).
According to Carla’s expectations, what will be the effect on the butterfly spread on the RBA’s yield curve?
- Increase
- Decrease
- No change
Explanation: Butterfly spread formula is:
2*Mid-term rates – Long-term rates – Short-term rates
In this case, Carla expects capital flows into Australia (more demand for bonds means yields decreasing). She expects that this impact will be most influential on mid-term rates, which means mid-term rates will fall more then LT and ST ones and the butterfly spread will shrink.
What’s the name of the move on the yield curve that Daniel expects?
- Bull steepening
- Bear flattening
- Bear steepening
Explanation: Daniel expects the Fed will struggle with inflation and will be forced to raise rates even higher, which is a bear movement. The yield curve going into inversion is an extreme case of flattening, and a deeper inversion means an even stronger flattening impact. Thus, the correct answer is bear flattening.